When Market Fails
This is my note for the course When Market Fails taught by Rebecca Stein at University of Pennsylvania.
Disclaimer
I am somewhat familiar with fundamental concepts of microeconomics and the power of free market. I am quite curious to learn about dark side of free market.
The notes is quite personal and maybe not follow exactly what has been taught, but also my personal adding views.
Notes
Week 1
Introduction
Cost & Profits
Recall to some basic mathematics:
profit = revenue - cost
revenue = price * quantity
cost = fixed cost + variable cost
Marginal productivity
marginal_productivity = change_output/change_input
Usually looks like below. The marginal productivity goes down because of the law of diminishing marginal productivity.
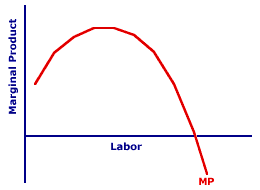
Marginal cost
Is reverse of marginal productivity

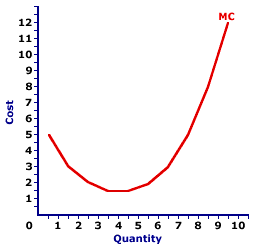
Perfect Competition
Definition
Four characteristics:
-
Produce standardized product
-
Industry has many buyers & sellers
-
No entry barrier
-
Full information
Any firm has no incentive to increase or decrease price –> price or all product are the same all the time.
Profit Maximization
Profit is maximized if marginal_revenue = marginal_cost
In perfect competition:
marginal_revenue = price
so marginal_revenue is a horizontal line while marginal_cost is a U-shape curve.

Proof
Why profit is maximized when marginal_revenue = marginal_cost
(quite easy)
Making Profit
Optimizing profit does not mean that you are making profit. E.g. if you are optimizing profit and the best value is -1, definitely you are losing money.
Short Run & Long Run
Short Run: the quantity of one (more) resource used is fixed.
Long Run: quantity of all resources can be varied.